Environmental Health and Safety


General Safety Training
Revised February 23, 2018
Outline
- Purpose
- Chancellor's Policy Statement
- Safety Responsibilities
- General Safety Rules
- Hazard Communication
- Reducing Hazard Exposure
- Fires and Fire Extinguishers
- Safety Support
Purpose
This training provides general safety guidance for LSUHSC faculty, staff and students. It is the first of four quarterly safety presentations issued via the Knowledge Delivery System as required by the State Office of Risk Management.
These quarterly safety presentations provide information generally applicable to all personnel. It is the responsibility of all supervisors to augment this training with site-specific safety training required in their work areas. For instance, while this presentation provides general guidance on Hazard Communication, personnel who work with hazardous chemicals must receive training on the hazards associated with those particular chemicals.
Chancellor's Policy Statement
The LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans is committed to providing a safe and healthy environment for all faculty, staff, students and visitors; and conducting its mission in compliance with all applicable environmental health and safety laws and regulations.
As Chancellor, I am responsible for ensuring that the Health Sciences Center operates safely to minimize health hazards, reduce the risk of injury, and maintain environmental compliance. Senior leadership and all supervisors share in this responsibility with me, and will ensure that all activities under their control are performed safely and in accordance with current policies and guidelines. A primary role of the Environmental Health and Safety (EH&S) Department is to oversee the safety and environmental programs, and provide consultative services; contact EH&S if you require assistance for any aspect of your safety and environmental programs.
Maintaining a safe and healthy environment requires the involvement of all faculty, staff and students. All members of the Health Sciences Center community are responsible for their own safety and shall set a personal example of safe practices for other members of the community. Your commitment to safety and environmental compliance plays a critical role in support of the Health Sciences Center's mission to provide world-class education, research and public service.
Safety Responsibilities
Vice Chancellors, Deans, Directors, and Department Heads shall implement the safety program in their areas of administrative responsibility and are responsible for the safety of the personnel under their supervision. They will ensure that these personnel are:
- Familiar with safe work practices.
- Informed of hazards in their work area.
- Provided with the proper training and supervision in order to perform their work safely.
Supervisors, Foremen, and Managers are also responsible for the safety of the personnel under their supervision and will:
- Train employees in the safe use of equipment and in safe work practices specific to the workplace.
- Correct any unsafe acts and unsafe conditions.
- Report and investigate accidents.
- Inspect their work areas for compliance with safe work practices and to identify potential hazards.
- Ensure new employees and employees who are assigned new tasks are trained on safety procedures before starting work.
Individual personnel are responsible for their personal safety and will:
- Follow prescribed safety rules and regulations.
- Immediately report safety hazards to their supervisor.
- Report to the supervisor all incidents/accidents, including "near misses", and any change in health status if it may be due to a job-related activity.
- Seek guidance from their supervisor if there is any uncertainty on any issue that may impact workplace safety.
The Environmental Health and Safety Department is the principal provider and coordinator of all LSUHSC safety requirements, to include:
- Providing resources to assist with the identification, evaluation, and control of hazardous situations.
- Providing assessments for research laboratories and shops working with potentially hazardous chemicals, biological or physical agents or processes.
- Providing general safety training, hazardous waste disposal, and occupational safety and health exposure evaluations.
- Developing and issuing rules and procedures.
General Safety Rules
Adherence to the following safety rules reduces the risk of mishaps:
- Don't smoke or use tobacco products on campus.
- Don't engage in horseplay.
- Before beginning work, notify your supervisor of any permanent or temporary impairment that may reduce your ability to perform in a safe manner.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards that can't be eliminated.
- Operate equipment only if you are trained and authorized.
- Inspect your workstation for potential hazards and ensure that equipment/vehicles are in safe operating condition before use.
- Immediately report accidents, near misses, and property damage to your supervisor regardless of severity.
- Immediately report any potentially unsafe condition or act to your supervisor.
- If there is any doubt about the safe work method to be used, consult your supervisor before beginning work.
- Follow recommended work procedures outlined for the job, including safe work practices outlined in the job safety analysis, standard operating procedure, or owner's manual.
- Maintain an orderly environment and work procedure. Store all tools and equipment in a designated place. Place scrap and waste material in a designated container.
- Fasten restraint belts. Do not use cell phones while operating a government vehicle or while using your personal vehicle or rental car for official business.
Hazard Communication
- You have a right to know of the hazards in your workplace and must be provided with the training and equipment necessary to protect you from these hazards.
- A substance is "hazardous" if classified as either a "physical hazard" (e.g., flammables, explosives) or a "health hazard" (e.g., carcinogen, hepatotoxic, mutagen).



- Each laboratory or shop that uses hazardous materials shall have a plan that addresses: proper handling, storage and disposal of the hazardous materials; maintenance of Safety Data Sheets; use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and other safety equipment (e.g., fume hoods); and site-specific training that is documented in writing.
- The site-specific training is required:
- Within 30 days of employment;
- When working in a new area;
- Whenever a new material or procedure is introduced into the workplace;
- Whenever the Department Head or Supervisor determines that refresher training is in order or
- At least annually.
- OSHA has implemented the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) of Hazard Classification and Labeling of Chemicals.
- GHS makes two primary changes to the prior program:
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) have been replaced by Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
- New labeling and pictograms.
Safety Data Sheets
- The previous chemical safety programs employed Material Safety Data Sheets, which are written in a variety of formats.
- GHS changed the name to Safety Data Sheets, and standardized the sections and information contained in the document.
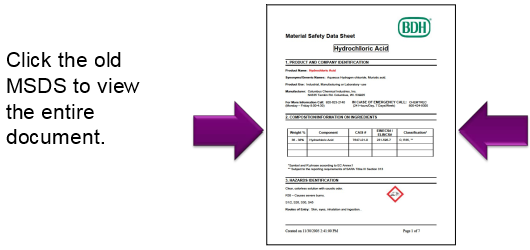
Safety Data Sheets
The new SDS format has 16 standardized sections:
- Identification
- Hazard(s) identification
- Composition of ingredients
- First-aid measures
- Fire-fighting measures
- Accidental release measures
- Handling and storage
- Exposure control/PPE
- Physical and chemical properties
- Stability and reactivity
- Toxicological information
- Ecological information
- Disposal considerations
- Transport information
- Regulatory information
- Other information
SDS-Example of the New Format
GHS Labels
- Similarly, the previous chemical labeling systems have non-standardized labels that look different for the same product. Labels also differ from country to country.
- Required GHS Product Label Elements:
- Product identifier and chemical name.
- Signal words - use "Danger" or "Warning" to indicate risk level.
- Pictograms.
- Hazard statements.
- Precautionary information.
- Supplier identifier.
- Although the label formatting is not standardized, all labels will contain the six items listed above.
Example Label
(Click or tap image for expanded view)
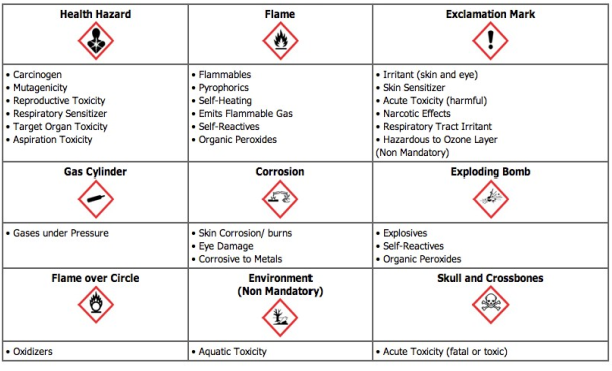
Pictograms
- The old hazard symbols, called "pictograms" were also different from country to country. GHS updates these to a standardized system for hazard communication.
- GHS uses nine pictograms, which contain a black picture, indicating a hazard, set inside a red diamond. The pictograms are shown below:
New Pictograms
(Click or tap image for expanded view)
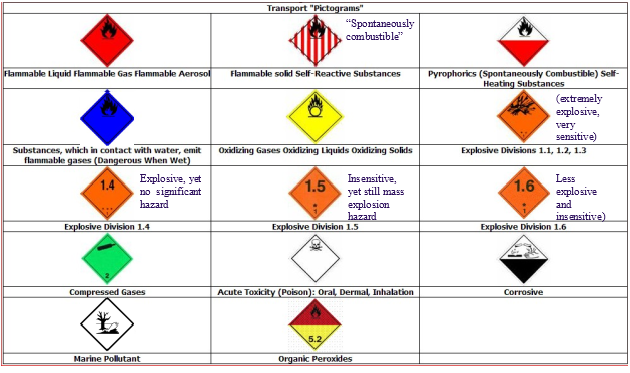
Transport Pictograms
When chemicals are being transported a different set of pictograms are used on the packaging.
- The Department of Transportation had already adopted the GHS transport pictograms, so nothing will change. Transport pictograms are shown below for reference.
- Where a transport pictogram appears, the GHS pictogram for the same hazard should not appear. Transport pictograms will occur on the outside of the box the chemical is packaged in.
(Click or tap image for expanded view)
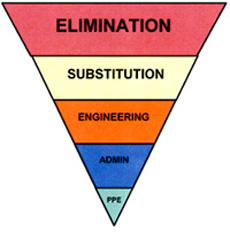
Reducing Hazard Exposure

The first consideration for controlling hazards is to eliminate the hazard or substitute a less hazardous material or process. When it is not possible to eliminate a hazard, you should control the hazard using the following methods (in order):
- Engineering.
- Administrative.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
Applying this hierarchy is a systematic approach to identify the most effective method of risk reduction. The highest-level feasible control should be selected.
Engineering Controls
- Engineering controls minimize employee exposures by either reducing or removing the hazard at the source or isolating the worker from the hazards.
- Examples of common engineering controls used at LSUHSC include chemical fume hoods, biological safety cabinets, and machine guards for power tools.
- Ensure all equipment requiring inspection and testing is currently certified.
- Maintain and follow the manufacturer's operating instructions for all engineering control equipment.
- Users of engineering control equipment must be familiar with their purpose, capabilities and limitations prior to use.
Administrative Controls
Administrative controls significantly limit daily exposure to hazards through policies and procedures that provide guidance for safe work practices and standard for behavior.
Examples include Job Safety Analyses (JSA) (see EH&S -400.04, Job Safety Analysis Policy for performance guidance), standard operating procedures (SOP), job rotation, training, signs and warning labels, personal hygiene, housekeeping and maintenance.
Administrative controls do not remove hazards, but help to limit or prevent exposure to the hazards.
Personal Protective Equipment
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a device or clothing worn by a worker to help prevent direct exposure to hazards.
- PPE is the least preferred method of protection, and should be used following implementation of engineering and administrative controls methods.
- Examples include respirators, hearing protection, gloves, lab coats and safety glasses.
- Proper selection of PPE is crucial since one type of PPE will not work with all types of hazards. Contact Environmental Health and Safety for assistance with PPE selection.
Fires
- If you see a fire or smoke, PULL the closest fire alarm pull station.
- ALERT others of the pending emergency and begin a calm and immediate evacuation of the building. Close the door(s) to your office or classroom to confine the fire.
- CALL University Police (568-8999) or 911 and provide:
- Your name and the telephone number.
- The exact location of fire or smoke.
- The type of fire (electrical, flammable liquid, trash, etc.).
- The extent of the fire (severity and/or amount of smoke).
- EVACUATE to the outdoor Emergency Evacuation Area.
Fire Extinguishers
- All buildings are equipped with automatic fire sprinkler systems. These systems activate when heat melts a sensing element in the sprinkler head.
- All buildings are also equipped with fire extinguishers, primarily type ABC extinguishers, which are effective against wood, paper and plastics; flammable liquids; and electrical fires.
- If you choose to use a fire extinguisher, ensure you follow the guidelines below.
Fire Extinguisher Guidelines
Never fight a fire:
- If the fire is larger than the volume of a typical trash can.
- If you must fight the fire with your back to an escape exit.
- If the fire can block your only escape.
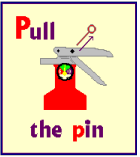
How to operate a fire extinguisher:
- Use the PASS method. (Pull, Aim, Squeeze and Sweep)



Miscellaneous Fire Guidelines
All open flames, open burns and the use of pyrotechnics/fireworks, both indoors and outdoors, are strictly prohibited at the Health Sciences Center except for:
- Classroom or laboratory: Bunsen burners may be used in the course when conducted under the supervision of the instructor.
- Hot Work Permit Program: Open flames are permitted when covered by the Hot Work Permit Program.
Safety Support
- If you need assistance performing a hazard assessment for your shop or lab, or if you identify a safety issue you can't correct yourself, contact Environmental Health and Safety at 568-6585 or safety@lsuhsc.edu.
- LSUHSC has four committees (General, Biological, Chemical and Radiation Safety) comprised of faculty and staff that address safety concerns. If you have an issue of concern that you would like to have a committee address, contact Environmental Health and Safety.