
Environmental Health & Safety
Laboratory Safety Training
Revised: February 17, 2017
Introduction
Laboratory Safety is a very important aspect of science. Without it, experimentation could result in very serious injury, if not death. To reduce the risks involved with experimentation, there are certain procedures that we should all follow as individuals and as a member of a group. It is important that the correct procedures are used in various situations, when handling hazardous or biological materials, when preparing, executing or cleaning up an experiment. It is also essential that you understand how to identify and use emergency equipment and protective gear.
Many laboratory guidelines are written based on experience – notably when things have gone badly wrong. Remember, you could be dealing with extremely dangerous and hazardous materials, so caution is required at all times.
Many laboratory accidents and problems are due to haste. In the lab however, it’s important to take your time - not only for safety reasons, but also to avoid wasting samples, money and time.
This training module is provided to guide you through and develop your understanding of Laboratory Safety. It is important to take your time to understand the procedures, concepts and reasons to make your laboratory as safe as possible.
Outline
- Housekeeping
- Fire Safety
- Hazardous Communication (HazCom)
- Hazardous Materials
- Chemical
- Biological
- Radiological
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eyewash and Shower Stations
- Gas Cylinder Safety
Housekeeping
- EATING or DRINKING is NOT ALLOWED in laboratories that contain either chemical, biological or radioactive sources.
- Dispose of trash when it is generated in appropriate containers. Prevent accumulation of trash within the laboratory.
- Don't place empty bottles and other trip hazards in a walkway.
- Keep chemicals and glassware away from the edge of counters.
- Immediately clean up all spills.


Fire Safety
- Exit signs must be lit and emergency lights operational.
- Know the location of the nearest fire extinguisher.
- Understand the hazard labels on door signs.
- Have MSDS sheets readily available.
- Flammable cabinet required if > 10 gals of any flammable present.
- Secure compressed gas cylinders.
- Do not impede fire sprinkler heads.
- Ensure electrical wiring lines are free of cuts and not fraying.
- In the event of an alarm:
- Secure any procedures that left unattended will pose a hazard.
- Know how to properly react in the event of a Fire Alarm.

Hazardous Communication (HazCom)
Recognition and Evaluation of Hazards
- You have the 'right to know' the hazards located in your workplace.
- Know the properties of chemical, biological and radioactive agents before you use or transport them:
- Toxicity (carcinogens, toxic, reproductive hazard)
- Flammability
- Reactivity/Incompatibilities
- Corrosive
- Unstable
- Radiation Emissions
- Bio-Safety Level 1-4 (Use of all Biological materials must be approved through Institutional Biosafety Committee)




Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)

- MSDS include:
- Chemical and Physical properties
- Toxicity, Health Effects
- Compatibility, Safe Handling and Storage
- Spill and Fire response
- MSDS's must be readily available, either in hard copy or on a computer hard drive.
- MSDS Internet Resources
Chemical Safety
The chemical safety program provides guidance and protocols to prevent injury to personnel, loss or damage to property, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations. Adherence to the basic principles of chemical safety reduces the risk of injury or chemical exposure.




Chemical Materials - Common Types
- Flammable/Combustibles
- Ethyl ether
- Methanol
- Acetonitrile
- Flammable Solids
- Activated charcoal
- Sulfur
- Phosphorus
- Oxidizers
- Silver nitrate
- Sodium iodate
- Ammonium persulfate
- Perchloric acid
- Nitric acid
- Toxics
- Osmium tetroxide
- Ethidium bromide
- Corrosives (Acidic/Basic)
- Sulfuric acid
- Nitric acid
- Acetic acid
- Potassium hydroxide
- Ammonium hydroxide
Chemical - Incompatibilities
- To avoid interaction between incompatible chemicals, all chemicals should be separated into compatible hazard groups, then placed alphabetically within each group.
- Since many chemicals present multiple hazards, consult the MSDS to determine the "primary" hazard class of a chemical.
- For more information on chemical storage, see Chemical Ordering and Storage Procedures.
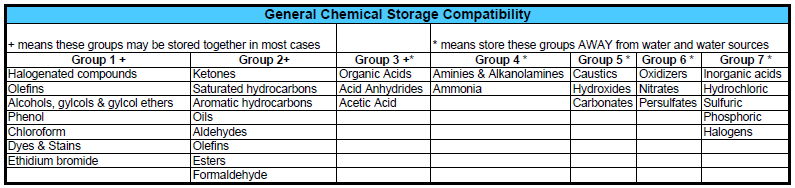
(Click or tap image for expanded view of table.)
Chemical - Storage
- When ordering chemicals, always order only what is needed; a six month supply is plenty.
- In chemical storage areas:
- Maintain chemical spill kits and fire extinguishers.
- Provide adequate shelving.
- Never store chemicals on floor.
- Store quantities of 10 gallons or more of flammable materials in an approved Underwriters Laboratory or Factory Mutual approved flammable storage cabinet.
Chemicals of Special Concern - Peroxide Forming
A wide variety of organic compounds can spontaneously form peroxides on exposure to air. Peroxides are sensitive to heat, friction, and shock.
- Label containers with receiving, opening and disposal dates.
- Store in amber, transparent bottles.
- Store away from heat sources and sunlight.
- Do not attempt to open a container or a peroxide forming compound if there are whitish crystals around the cap and/or in the bottle because it may be potentially explosive.
- For additional information on peroxide forming chemicals see Chemical Ordering and Storage Procedures Appendix B.
Chemical - Engineering Controls
Chemical Fume Hoods are an important tool used to minimize exposure.
- Hoods must be available for use and functioning efficiently at all times.
- Work with volatile chemicals in fume hoods when feasible.
- Fume hoods are not a place to store chemicals or equipment. Fume hoods are not designed to collect particulates.
- If your hood is not functioning properly, create On-line Service request.

Prior to Using a Fume Hood
- Check the hood certification sticker on the front of the hood to ensure that the air flow is between 80 and 150 feet per minute when tested.
- Check visual alarms to ensure that the hood is functioning properly.
- Hold a Kimwipe or tissue at the face of the hood to ensure air is flowing into the hood when the fume hood is turned on.
- Check baffles to be sure slots are open and unobstructed by equipment or containers.
- Ensure that all chemicals and equipment are at least six inches behind sash.
- Decrease turbulence by opening / closing sash slowly; avoid swift movements inside / outside of the hood.
- Keep sash as low as possible (closed when not in use).
Chemical - Waste Disposal
- When collecting waste, compatible waste streams may be collected in one container; never mix incompatible wastes.
- Chemical disposal containers:
- Use containers that are in good condition and are compatible with waste storage type.
- Always keep the container closed during storage; never leave a waste container open with a funnel in it.
- Use containers with capacities of one gallon or less and never over fill them.
- Label all waste containers with:
- The words "Hazardous Waste".
- Principle chemical constituents.
- Date that waste was first placed in the container.
- To dispose of batteries:
- Place in individual plastic bags or cardboard boxes for collection.
- Cover terminals with tape if not placed in individual bags or boxes.
- For disposal of mercury containing equipment, place all equipment containing elemental mercury in a plastic bag and seal.
- Waste Pick-up:
- Create On-line Service request for every hazardous chemical waste pick-up.
- For additional information review the Chemical Waste Management Procedures.
Chemical - Spill Response
- Regardless of volume spilled, do not attempt to clean up a spill if the chemical is unknown or if known chemical is extremely toxic. For more information see Chemical Spill Response Policy.
- Call Chemical Safety Officer at 504-952-1337 for assistance.
- Use your Chemical spill kit. If you need to order one create an On-line Service request.
Biological Safety
Biosafety is the application of combining laboratory practices, procedures, facilities, and safety equipment to protect human health and prevent release of biological materials into the environment.
Biological materials are defined as any biologically-derived materials which, either by accident or design, contain biological agents.

Biological Materials - Common Types
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Viral Agents
- Parasites
- Rickettsidal Agents
- Bacterial Toxins
- Prions
- Transgenic Animals or Plants
- Human or Primate Cell Cultures
- Recombinant DNA
Biological Safety - Institutional Biosafety Committee
- Prior to beginning work, all labs at LSUHSC using rDNA, infectious material, or other biological materials must contact the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC).
- IBC reviews all protocols involving biohazards.
- Non-exempt labs will be inspected to assure they meet the CDC/NIH guidelines.
- LSUHSC Biosafety Committee Website
Biological - Exposure
Most common types of exposures:
- Needle Sticks
- Exposure to eyes, mouth and mucous membranes
- Bioaerosols
- Spills
Biological - Engineering Controls
Biological Safety Cabinets (BSC) are an important tool used to control bioaerosols and minimize exposure.

- BSCs are designed to protect the product, worker, and environment.
- Laminar flow hoods only protect the product.
- BSCs remove particulates, not chemical vapors.
- All Biosafety cabinets must be certified annually, prior to initial usage, and if moved.
- Contact EH&S before purchasing a new cabinet for help in selecting the appropriate cabinet.
Biological - Waste Disposal
Biohazardous waste includes the following general categories:
- Cultures and stocks.
- Pathological waste.
- Human and animal blood and blood products.
- Used and unused sharps (e.g., needles, syringes, pipettes, scalpels, broken glass, slides, cover slips).
- Animal waste (e.g., carcasses and bedding).
- Isolation wastes. Any other refuse, which has been mingled with any of the waste(s) listed above.
Never place chemicals, chemical bottles, radioactive materials, or other trash in biowaste containers.
Waste containers for:
- Biohazardous waste
- Use boxes with red biohazard plastic liners.
- Biohazard boxes should not be overfilled or made too heavy for transport.
- Biohazardous sharps
- Place biohazardous sharps (e.g., needle, glass, scalpel) inside a sealable, leak-proof sharps container.
- Full needle boxes should be placed inside the biohazard box for disposal.


Biological - Spill Response
- Response to biohazard spills depends on:
- Actual agent and associated risks.
- Agent's Biosafety level.
- Amount of material spilled.
- Type of the spill.
- Location of the spill.
- Call Biological Safety Officer at 504-952-1337 or see the Biological Spill Response Policy.
Radiological Safety
Radiation Safety is the science of protecting people and the environment from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation, which includes both isotope particle radiation and high energy electromagnetic radiation.
Ionizing radiation can only be used in approved licensed laboratories.

Radiological Materials - Common Types
- Beta Emitters
- Carbon 14 - (C14)
- Hydrogen 3 - (H3)
- Sulfur 35 - (S35)
- Phosphorous 32 - (P32)
- Gamma Emitters
- Iodine 125 - (I125)
- Cesium 137 - (Cs137)
- X-Ray Emitters
- Dental X-ray machines
- Medical X-ray machines
Radiological - Institutional Radiation Safety Committee
- Prior to beginning work with any radiation source, all labs investigators must fill out a Radiochemical Use Application Form.
- The Radiation Safety Committee reviews all applications and approves/disapproves three year permits.
- Approved labs will be inspected every quarter by the LSUHSC Radiation Safety Officer to ensure they meet Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality guidelines.
- Call Biological Safety Officer at 504-952-1337 or see the LSUHSC Radiation Safety Committee Charter.
Radiological - Exposure
- Most common types of exposures:
- Exposure to skin, eyes, mouth and mucous membranes.
- Inhalation of Iodine fumes.
- Spills
- X-ray incident exposures.(Dental School and Medical machines)
- How to reduce your exposure:
- Time
- Distance
- Shielding
- Housekeeping
Radiological - Incompatibilities
- Never mix different half-life radiation waste together. Note: Only H3 and C14 may be combined due to long half lives and low beta energies.
- Try to mix liquid isotopes with aqueous solutions only, since mixing radiation liquids with chemicals makes it more difficult to dispose of this "mixed" waste.
Radiological - Engineering Controls

- Acrylic shielding for Beta shielding (H3, C14, S35 and P32).
- Leaded Acrylic shielding for Low Level Gamma (I125).
- Lead Bricks for Moderate to High Level Gamma used for storage (I125 and Cr51).
- Lead Aprons for X-ray shielding (Dental and Medical X-ray machines). Cultures
Radiological - Waste Disposal
- For disposal of radioactive liquids, place all liquids in five gallon carboys or one gallon plastic jugs and adhere the Radioactive waste form.
- For disposal of radioactive solids, use supplied cardboard boxes with plastic liners and adhere radioactive waste form externally.
- For radioactive hazardous waste pick-up create On-line Service request.
Radiological - Spill Response
- Radiation spill classifications:
- Minor Spill - Incident which involve the release or spillage of less than 100 microcuries (uCi) of a radionuclide.
- Major Spill - Incident which involve the release or spillage of more than 100 microcuries (uCi) of a radionuclide.
- Follow the S.W.I.M.S. procedure:
- Stop and think. Stop working. Stop the spill.
- Warn others.
- Isolate the area.
- Monitor yourself carefully and completely.
- Stay in or near the area until help arrives.
- Call Radiation Safety Officer at 504-314-5989 for assistance or review Radiation Spill Response Procedures.
Personal Protective Equipment
- Do not wear shorts or any clothing that exposes any skin other than arms or face.
- Do wear the appropriate PPE for the situation:
- Gloves
- Splash Goggles/Face Shields
- Lab Coats
- Respirators
- Provide proper storage of all PPE.
Gloves

- The type of glove (material) used is dependent upon the chemical being handled.
- When using corrosive or toxic chemicals the gloves should be long enough to protect the forearm.
- Long gloves can be cuffed at the bottom to help prevent chemicals from running down the arm.
- Proper glove selection information can be accessed online at Ansell 8th Edition Glove Guide.
Splash Goggles and Face Shields
- Splash Goggles must be worn whenever lab workers are using liquid chemicals that could injure the eyes, including heated liquids.
- Face Shields must be worn in conjunction with splash goggles if lab workers are using chemicals that could splash and corrode or burn the face, or when using toxic chemicals that could be splashed and absorbed through the skin.

Respirators
- Respirators must be worn when there is potential exposure to contaminants such as bioaerosols, dry chemicals and airborne particulates.
- You must know the type of respirator needed.
- You must not have hair on your face for proper seal.
- You must have medical clearance and be fit-tested.
- Fit Tests are performed by EH&S.


Lab Coats
Lab Coats must be worn when there is potential exposure to:
- Chemicals
- Biologicals
- Radiologicals

Storage Method
Personal protective equipment should be stored in a manner that protects the equipment from:
- Dust
- Sunlight
- Excess moisture
- Extreme temperatures
- Deformation
- Chemical degradation
- For more information see the PPE Policy.

Eyewash and Shower Stations


- Suitable eyewash & shower stations must be immediately accessible and usable to lab personnel that are using chemicals that could injure the eyes/skin.
- For more information see the Emergency Eyewash and Shower Policy.
Compressed Gas Cylinders

- Cylinders could act as a projectile if dropped and damaged.
- Cylinders should be secured. Secure cylinders to stationary objects (like a wall).
- Remove regulators and install valve protection caps when cylinders are not in use.
- If cylinder not properly secured, create On-line Service request.
Liquid Nitrogen/Cryogenic
- (LN ) is extremely cold. -320F (-196C)
- Displaces oxygen.
- Expands rapidly.
- Protect eyes and skin with goggles, gloves, shoes.

- Safe handling tips for (LN2)
- Do not allow to touch bare skin.
- Do not seal containers.
- Transfer liquid with care.
- Transport containers with care.
- Handle containers with care.
- Emergency Preparation Liquid Nitrogen Supply and Safety Plan
Thank you
- This and other safety presentations are posted on the Environmental Health and Safety homepage under Safety Training
- If you have comments or questions on this training, contact EH&S. e-mail