Legacy CMS Web Accessibility Guidelines
Building Accessible Web Pages
The LSU Health New Orleans web template is accessibility compliant with standards, and our in-house content management system (CMS) has tools that make building accessible websites easier. As a site editor, you should review this page to ensure your site is accessible. The best way to review your site is to use third party checkers. One that we recommend using is http://wave.webaim.org/.
Table of Contents
Checking Web Pages for Accessibility
Page Title
Page titles define the title of the document and are required in all HTML documents.
Page titles make web pages more accessible because:
-
Individuals with visual disabilities will benefit from being able to differentiate content when multiple Web pages are open.
-
Individuals with cognitive disabilities, limited short-term memory, and reading disabilities also benefit from the ability to identify content by its title.
-
Individuals with severe mobility impairments rely on audio when navigating between Web pages.
For the page to be accessible, the title must be brief and unique from other pages on the site.
Editing a Page Title in CMS
- Click "Edit Page" at the bottom of the page
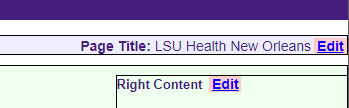
- Click the "Edit" button at the top of the page next to the section named "Page Title" (see image below).
- Enter the title text and click the "Submit" button.
Headings
Headings format text to separate sections and make things easier to read (like "Headings" right above this sentence). Usually, the heading text is larger and bold. LSUHSC sites contain three different levels of headings, each with their own size.
Headings make websites more accessible for people who have difficulty with mobility since headings allow them to jump quickly around the page.
To make the page easier to read, headings should use a meaningful hierarchy. An example follows:
- Heading Level 1
- Heading Level 2
- Heading Level 3
- Heading Level 3
- Heading Level 2
- Heading Level 3
- Heading Level 2
A heading should usually be a title or subtitle, which will logically separate the sections of the page.
Creating Headings in CMS
- Click "Edit Page" at the bottom of the page.
- Click the "Edit" button at the section that you would like to edit.
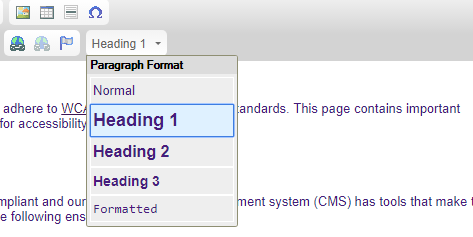
- Click the drop-down box at the top right in order to change text into three different types of headings. (see image below).
Alternative Text for Images
Alternative text provides a textual alternative to non-text content in web pages such as an image.
Alternative text is used by the visually impaired to understand the purpose of the image.
In order to make a page more accessible, every image should contain alternative text.
Creating Text Alternatives in CMS
- Click "Edit Page" at the bottom of the page
- Click the "Edit" button at the section that you would like to edit.
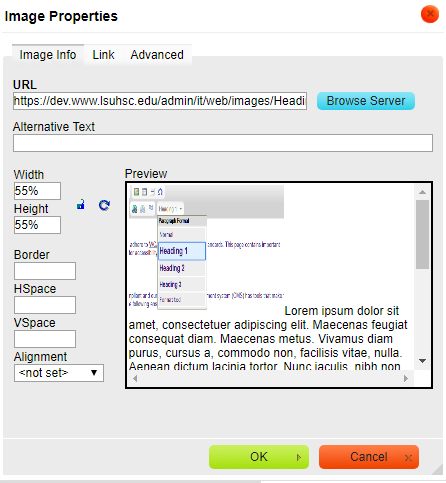
- Right click on an image and click "Image Properties."
- Edit the text in "Alternative Text" (see image below) and click "OK."
Meaningful Link Text
A link text is the text that is contained in a hyperlink.
Screen readers read out link text to the visually impaired so that they can navigate through the links.
In order to make the page more accessible, the link text should be short and unique.
Creating Meaningful Link Text in CMS
- Click "Edit Page" at the bottom of the page
- Click the "Edit" button at the section that you would like to edit.
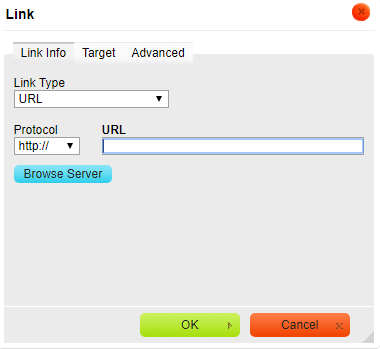
- Highlight the text you want to link and select the "Link" button (to the left of the headings drop-down box).
- Add the URL that you want to link and click the "OK" button (see image below).
Video Captions
Videos should include closed captions to enhance accessibility. Below are methods for accomplishing this:
- Host publicly accessible videos on YouTube which has built-in tools for automatically adding closed captioning. Reference - information on how to add, edit, and review closed captions in YouTube
- Host videos restricted to internal users on MediaSite. MediaSite is hosted internally and can limit access but does not yet
include built-in closed captioning capabilities. Until this feature is available,
use other means to include CC such as:
- Third-party solutions like https://www.rev.com
- Video editing software like Adobe Premiere that accepts video caption files (.scc)
For more information on working with web videos, please see our Best Practices. If you have any questions please send your request to Webmaster.
Accessible Tables
Tables are an assortment of rows and columns that hold data.
People with visual disabilities use screen readers to access and understand tables.
To make your site accessible, it is important that tables are not used for design. This can confuse a screen reader and make it difficult for the visually impaired to read a page.
Paragraph and Line Breaks
There are two different ways tags to separate text. (<p> and <br>)
In order to make your site more accessible, the <p> tag should be used to separate paragraphs.
This makes the site more accessible to the visually impaired since screen readers cannot move between <br> tags. This makes it difficult for screen readers to read paragraphs of text.
To avoid using the <br> tag while in CMS, use the "enter" key to separate text into paragraphs. By pressing the "shift" and "enter" keys at the same time, the <br> tag is used.
Checking Web Pages for Accessibility
There are several third party tools that can be used to check your pages for accessibility.
One that we recommend using is http://wave.webaim.org/.
You can also check for accessibility in the latest version of Google Chrome with developer tools. This can be done by:
- Right click the page and select "Inspect"
- Select the "Audits" tab
- Select "Perform an audit.."
- Make sure that "Accessibility" checkbox is checked and select the "Run audit" button.
