To more accurately reflect the myriad sources available, the Electronic Journals List is now the E-Journals & E-Books A to Z List. When it was introduced as a Library resource in 2008, the majority of titles included were journals, but as more and more types of resources other than journals have made their way onto the list, a new moniker became necessary.
The E-Journals & E-Books A to Z List provides links to many of the journals and books available electronically through Library subscriptions, titles that come via full-text databases like Academic Search Complete, and numerous free journals and books from sites such as Project Gutenberg.
Even though there are tens of thousands of resources available on the list, we are unable to include everything on it so the Library’s Catalog is still a good place to start your search when you need a book or journal.
Access Emergency is unavailable due to technical difficulties on publisherÔÇÖs site.
We apologize for your inconvenience.
*Access was restored on Friday, October 4th at 11 am *
Scirus, Elsevier’s free search engine, will be shutting down in January 2014. In a message to users, they stated no more content will be added starting immediately.
We will keep the links active for the WebBridge Link Resolver until Scirus is completely discontinued.
Update: All Springer LINK journals and books are now working. If you encounter any problems, please contact us.
September 9: We are unable to access any of the journals or books published by Springer that are available through Springer LINK. We are working to have this problem resolved and will update as soon as possible. For a list of affected journals, check this link.
The Springer Protocols, which are hosted on a different platform, are working fine.

MosbyÔÇÖs Nursing Consult is launching two new content areas.?á As a result, the web site will undergo maintenance on Sunday, August 18th from 12:00 am to 6:00 am.?á During this time, the site will be unavailable.?á When MosbyÔÇÖs Nursing Consult relaunches at 6:00 am, you will have access to two new areas in the Calculators & Tools section: Labs & Diagnostics and Scales.
If you encounter problems after the maintenance has been completed, please contact a library staff member and someone will get back to you during regular library hours.
Thanks for your patience while this product is upgraded!
 LSUHSC-NO Libraries have added 15 digital books to its customized R2 Library from Rittenhouse Book Distributors. Links to each digital version are accessible through a simple search in the LSUHSC catalogÔÇÖs holdings.
LSUHSC-NO Libraries have added 15 digital books to its customized R2 Library from Rittenhouse Book Distributors. Links to each digital version are accessible through a simple search in the LSUHSC catalogÔÇÖs holdings.
As a web-based ePlatform, the R2 Digital Library offers seamless eBook access on desktop computers, laptops, tablets, smartphones and web-capable eReaders. An extensive image library, deep linking and integrated drug information provide an enhanced experience for the user. The R2 Digital LibraryÔÇÖs user interface is optimized for the health sciences.
The newest R2 eBooks that are now available through our Libraries are:
- Resolving Ethical Dilemmas, by Bernard Lo, 5th edition: 2013. Also in print at: WB 60 L78r 2013 (Isch?® Reserve).
- Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology, by Vincent DeVita Jr., Theodore Lawrence, & Steven Rosenberg, 9th edition: 2011. Also in print at: QZ 200 D49c 2011 (Isch?® Reserve).
- The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations: Musculoskeletal System (Vol 6, Pt 1: Upper Limb), by Joseph Iannotti & Richard Parker, 2nd edition: 2013. Also in print at: QZ 17 N38n 2013?á Pt.1 (Isch?® Stacks).
- The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations: Musculoskeletal System (Vol 6, Pt 2: Spine & Lower Limb), by Lynn Lippert, 2nd edition: 2013. Also in print at: QZ 17 N38n 2013?á Pt.2 (Isch?® Stacks).
- Essentials of Medical Genetics for Health Professionals, by Laura Gunder & Scott Martin: 2011.
- Gerontology for the Health Care Professional, by Regula Robnett & Walter Chop, 2nd edition: 2010.
- Clinical Manual of Emergency Psychiatry, by Michelle Riba & Divy Ravindranath, 1st edition: 2010.
- Cases in Clinical Medicine, by Pamela Moyers Scott: 2012.
- Challenging Cases in Pediatric Ophthalmology, by David Granet, Shira Robbins, & Leslie Baber: 2013.
- Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, by Richard Mitchell, Vinay Kumar, Abul Abbas, Nelson Fausto, & Jon Aster, 8th edition: 2012.
- Robbins & Cotran Atlas of Pathology, by Edward Klatt, 2nd edition: 2010.
- LippincottÔÇÖs Primary Care Musculoskeletal Radiology, by George Bridgeforth & John Cherf: 2011.
- Physician Assistant, by Ruth Ballweg, Edward Sullivan, Darwin Brown, & Daniel Vetrosky, 5th ed: 2013. Also in print at: W 21.5 B21 2013 (Isch?® Reserve).
- Concise Histology, by Leslie Garner & James Hiatt: 2011.
- Pediatric Nursing Procedures, by Vicky Bowden & Cindy Greenberg, 3rd edition: 2012.
We’re pleased to offer yet another way to help you get to Library resources in the form of the LibX browser extension. Available for Chrome and Firefox, this add-on has a number of features, including quick ways to search databases and re-load pages for more seamless off-campus access. Download the LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans Library Edition of LibX at http://libx.org/editions/6F/A1/6FA10750/libx.html.
More information about this browser extension, its features, and other tips can be found on the Library’s LibX LibGuide.
UPDATE: We have been informed by those who manage the list that this is the expected behavior. You will most likely see titles that do and do not begin with the desired term when you search the list and choose the “Begins with” option.
The “Begins with” search option for the Electronic Journals List is currently not functioning correctly. We have been in contact with those who manage the list, and they are presently working to solve the problem. We will update as soon as we hear more regarding this issue.
If you need assistance with this or any other Library resources, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Update: As of June 27th, the link resolver is once again available for use with Scirus.
June 11th: The WebBridge Link Resolver is currently not available through Scirus. The problem is being investigated and will hopefully be fixed soon.

We are no longer having technical difficulties with the OCLC First Search/WorlCat database.?á Should you run across any abnormalities, please let us know!?á Thanks!
OCLC FirstSearch/WorldCat is a database of bibliographic records for materials held by libraries and institutions around the world. For more information visit the OCLC web page: http://www.oclc.org/firstsearch.en.html.
For more information on how to access FirstSearch via our library, please visit our FirstSearch web page: http://www.lsuhsc.edu/no/library/ss&d/data/worldcat.html
The Library has a new mobile website. You can access the site through the “Mobile Isch?®” link on the homepage. When you go to the homepage (http://www.lsuhsc.edu/no/library)?áon any mobile device, a screen will prompt you to select the Library Mobile Site. The site includes access to the library catalog (INNOPAC), some of our most popular databases in mobile format, electronic journals, research guides, the web chat with a librarian service, library hours, contact information, locations, and frequently asked questions. If you have any feedback about the mobile site, please e-mail jbroo8@lsuhsc.edu.


We are experiencing technical difficulties with the OCLC First Search/WorlCat database. We have reported the problem to our support team. One of the main inaccuracies we are seeing is that books not owned by our library are displaying as if we are holders.?á We’ll keep you posted as we find out more information!
OCLC FirstSearch/WorldCat is a database of bibliographic records for materials held by libraries and institutions around the world. For more information visit the OCLC web page: http://www.oclc.org/firstsearch.en.html.
For more information on how to access FirstSearch via our library, please visit our FirstSearch web page: http://www.lsuhsc.edu/no/library/ss&d/data/worldcat.html
 The fifth edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is now available through the PsychiatryOnline database. The DSM-5?« is the product of more than ten years of effort by hundreds of international experts in all aspects of mental health.
The fifth edition of the American Psychiatric Association’s (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is now available through the PsychiatryOnline database. The DSM-5?« is the product of more than ten years of effort by hundreds of international experts in all aspects of mental health.
The DSM has been the most comprehensive resource used by health professionals, social workers, and forensic and legal specialists to diagnose and classify mental disorders. In the United States the DSM serves as a universal authority for the diagnosis of psychiatric illnesses. Treatment recommendations, as well as payment by health care providers, are often determined by DSM classifications, so the appearance of a new version has significant practical importance.
The DSM-5?« was published on May 18, 2013, superseding the DSM-IV?«, which was published in 1994. The development of the new edition began with a conference in 1999, and proceeded with the formation of a Task Force in 2007, which developed and field-tested a variety of new classifications. In most respects DSM-5?« is not greatly changed from DSM-IV?«. Notable innovations include dropping Asperger syndrome as a distinct classification; loss of subtype classifications for variant forms of schizophrenia; dropping the “bereavement exclusion” for depressive disorders; a revised treatment of gender identity issues; and a new gambling disorder.
?áAlso featured in PsychiatryOnlineÔÇÖs DSM Library are:
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV-TR?«)
- DSM-IV-TR?« Handbook of Differential Diagnosis
- Cases from DSM-IV-TR?« Casebook and Its Treatment Companion
PsychiatryOnline is a web-based psychiatry portal that includes books, journals, textbooks, practice guidelines, self-assessment, clinical and research news and medication patient handouts. LSUHSC-NO faculty, staff, and students can access PsychiatryOnline on campus, or off campus with use of a valid LSUHSC library barcode and PIN. Visit our PsychiatryOnline electronic resource page for more info. You can also connect to PsychiatryOnline by visiting the LibraryÔÇÖs website, and then selecting the ÔÇ£Online ResourcesÔÇØ category.
Books, E-Book News, E-Resource News, Library News, New Find, Psychiatry, Publication Alert, Tools | Permalink | Comments Off on New edition of the DSM available through PsychiatryOnline | Posted Monday, June 10, 2013 by Woodruff, Amy
The latest addition to our lineup of databases and sites configured to work with the WebBridge Link Resolver is Scirus. However, you must set up the preferences in Scirus to show the link resolver icon whether you are searching the site on- or off-campus.
First, select “Preferences” from the Scirus main page:
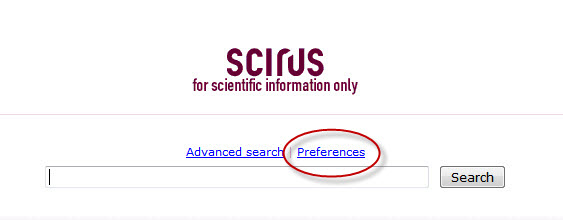
Next, under the “Library Partner Links” change the radio button to “Enable,” select “L” from the alphanumeric list, and then select the entry for “LSU Health Sciences Center New Orleans Libraries” :
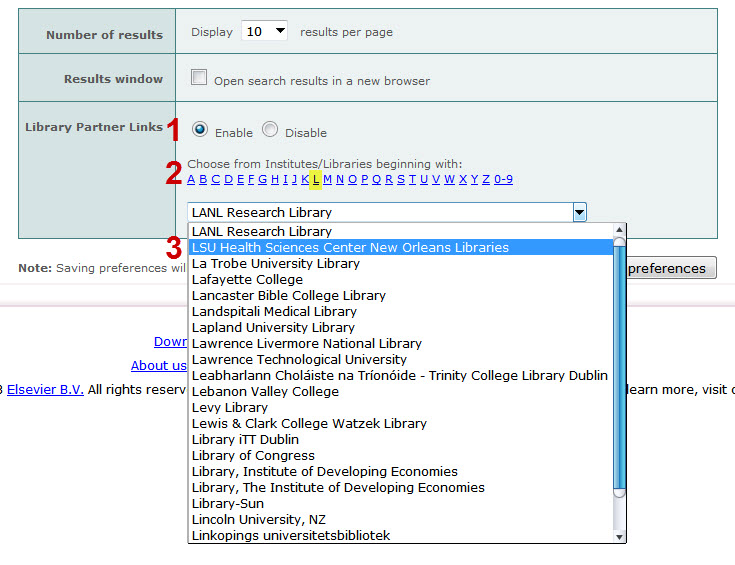
Once you’ve made these changes, click the “Save Preferences” button:
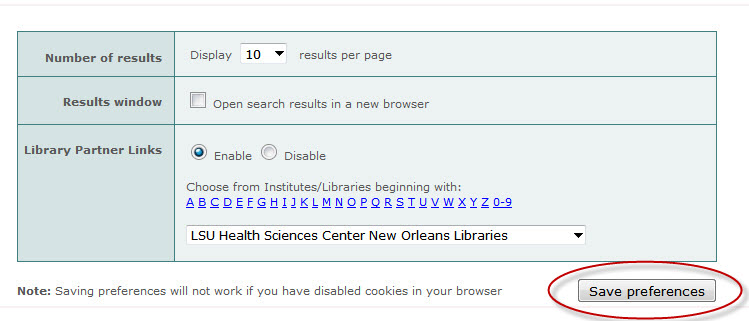
The WebBridge Link Resolver icon will display only for journal articles as long as you do not clear the cookies from your browser:

If you need any more information about the link resolver, please check out the WebBridge Link Resolver LibGuide or our newly-updated link resolver handout.

The Library is pleased to announce that we now have CINAHL Complete! CINAHL Complete is EBSCOÔÇÖs most comprehensive access point for full-text nursing and allied health literature. It replaces CINAHL Plus with Full Text, but donÔÇÖt worry, you wonÔÇÖt have to learn how to use a new product; the look and functionality are the same. What is different is that now there are more?áfull-text journals?áand indexed titles.?á “How many?ámore?” you ask!?á Well,?áthere are over 550?ámore?áfull-text journals and over 150 additional indexed journals.?á In all, CINAHL Complete includes access to over 1,300 full-text journals and includes indexing for over 5,400 journals. Our subscription also includes over 130 Evidence-Based Care Sheets, 170 Continuing Education Modules, and more. To see a complete list of journals available, you can click on ÔÇ£PublicationsÔÇØ at the top of the CINAHL Complete screen.
?á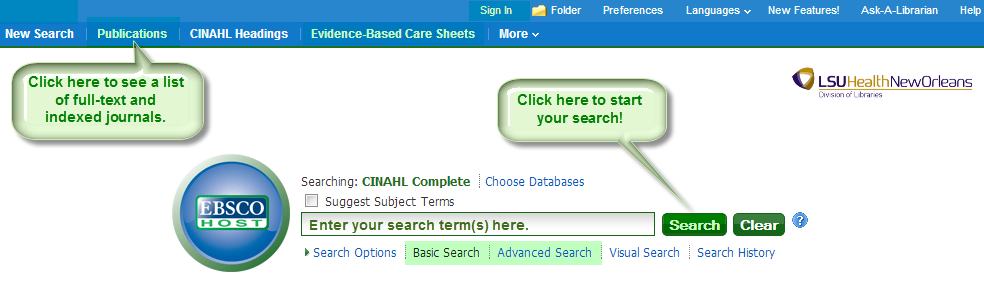
LSUHSC-NO faculty, staff, and students can access CINAHL Complete on or off campus. Visit our CINAHL Complete electronic resource page for more information: http://www.lsuhsc.edu/no/library/ss&d/data/cinahl.html.?á?á
Remember, many of the core journals are listed in the library catalog, INNOPAC, and you can link directly to a journal?áand browse available issues from there, too.?á And all these journals are listed in our EBSCO A to Z list.
For further assistance searching CINAHL Complete, contact a reference librarian on duty.

 myLSUHSC
myLSUHSC







