As soon as the human body became an object of study and curiosity, art attempted to render it, inside and out. The recreational artist may depict a scene of illness or portraiture, while the specially-commissioned medical artist records anatomical structure and surgical procedure for purposes of instruction, collaboration, and publishing. Well-known pioneers of the modern practice of medical illustration include Leonardo Da Vinci and Andreas Vesalius; their legacy continues well into contemporary culture in tandem with advances in photography and various other image-capturing technology to create a comprehensive visual understanding of medical practice.
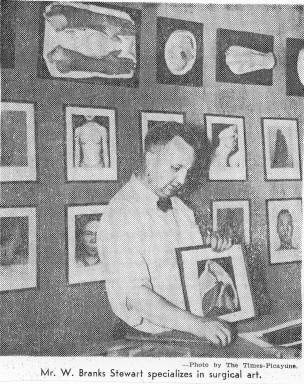 LSU Medical School employed its own Medical Arts Department, headed by William Branks Stewart from 1933 until his death in 1950, to observe and document cases as needed. ÔÇ£Would You Like a Portrait of Your Appendix?ÔÇØ asks a Times-Picayune article from 1946–a memorable keepsake, indeed (though you might enjoy this plush version more). Mr. StewartÔÇÖs body of art includes drawings, paintings, photographs, plaster molds, and even animations for use as visual aids in demonstration, in print, and in the classroom. Our Library has made available a digitized collection, aptly named the William Branks Stewart Collection, as a sampling of his works.
LSU Medical School employed its own Medical Arts Department, headed by William Branks Stewart from 1933 until his death in 1950, to observe and document cases as needed. ÔÇ£Would You Like a Portrait of Your Appendix?ÔÇØ asks a Times-Picayune article from 1946–a memorable keepsake, indeed (though you might enjoy this plush version more). Mr. StewartÔÇÖs body of art includes drawings, paintings, photographs, plaster molds, and even animations for use as visual aids in demonstration, in print, and in the classroom. Our Library has made available a digitized collection, aptly named the William Branks Stewart Collection, as a sampling of his works.
Mr. StewartÔÇÖs services were often requested in order to document rare cases and new procedures for later study and review. According to the above article, he would often take the time to familiarize himself with the entire operation in as many as twelve separate instances. A firm understanding of the techniques involved in a procedure and how best to communicate those steps to a student, he found, are necessary skills for the successful medical illustrator. When asked to contextualize his work, Mr. Stewart related his duties to those of an archaeologist with one important difference:” none of them ever had to look down a gastroscope!”
In addition to his professional position as Head of Medical Arts and contributor of drawings to the LSU student-run newspaper, The Tiger, William Branks Stewart was a member of the New Orleans Arts League and the Association of Medical Illustrators. By 1946, he had illustrated eleven textbooks by LSU professors, made plastic prosthetic eyes to replace glass ones, taken moulages (plaster or wax casts) of skin lesions, and even painted names on office doors. He submitted artwork to the Delgado Museum (now the New Orleans Museum of Art), an example of which can be seen here (be sure to take a look at the inscription on the reverse side).
A graduate of the Glasgow School of Arts in Scotland, it appears Mr. Stewart was destined for great things. In a prompted address to readers of The Tiger (page two), he candidly states, “Why did I study art? To make big money? Am I making it? To dodge work? Am I dodging it? Have I failed? No, I am doing something I enjoy, among people I enjoy, and in what I consider to the be most interesting city in America. So what the h—.”
Medical illustrations continue to be of great importance to our students as often photographs alone cannot provide a clear picture of the field under observation. Or, if you are like me, you may appreciate less “icky” renderings of our vicera.
Interested in learning more about the history of medical illustration, art in medicine, or anatomy study? Be sure to take a look at our Library Catalog!
Glimpse of the Past is an ongoing project to promote the Louisiana Digital Library effort. This Month in History will present for your reading pleasure a closer look into a newspaper clipping of note from our Digital Collections and articles relating to the LSU Medical School.

 myLSUHSC
myLSUHSC

 These E-books and many more are included in the
These E-books and many more are included in the  EBSCOhost E-books may be printed, saved, or emailed one chapter at a time.
EBSCOhost E-books may be printed, saved, or emailed one chapter at a time.
 AccessMedicine E-books may be printed one chapter at a time.
AccessMedicine E-books may be printed one chapter at a time.